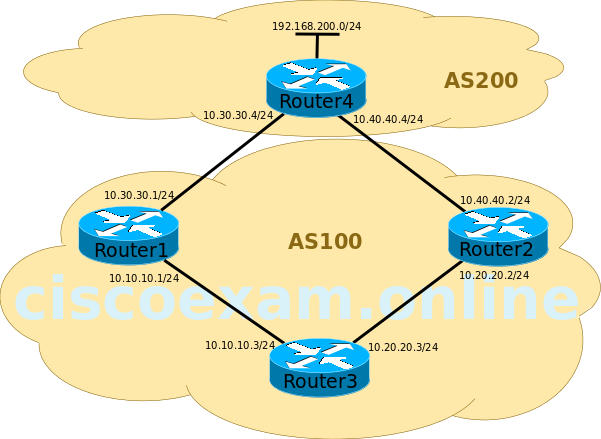
You administer the network shown in the diagram above. All routers are running BGP, and all attributes are set to the default values.
You want to ensure that Router3 sends packets to the 192.168.200.0/24 network through Router2.
Which of the following command sets can you issue to accomplish your goal?
| A. |
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.20.20.3 weight 45000
| |
| B. |
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.40.40.4 weight 45000
| |
| C. |
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 400
| |
| D. |
Router2(config)#route-map map1 permit 10
Router2(config-route-map)#set local-preference 500
Router2(config-route-map)#exit
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.20.20.3 route-map map1 in
| |
| E. |
Router2(config)#route-map map1 permit 10
Router2(config-route-map)#set local-preference 300
Router2(config-route-map)#exit
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.40.40.4 route-map map1 in
|
You can issue the following command set to ensure that Router3 sends packets to the 192.168.200.0/24 network through Router2:
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#bgp default local-preference 400
Alternatively, you can issue the following command set to accomplish your goal:
Router2(config)#route-map map1 permit 10
Router2(config-route-map)#set local-preference 300
Router2(config-route-map)#exit
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.40.40.4 route-map map1 in
When a router has multiple paths to a destination and weight values of the routes are equal, the route with the highest local preference is preferred. Typically, the multiexit discriminator (MED) value is used to indicate a preferred path into an AS with multiple entry points and is advertised to external Border Gateway Protocol (eBGP) routers.
However, local preference is considered before the MED value, so you can configure the local preference to prefer one route over another.
Issuing the bgp default local-preference 400 command configures Router2 to advertise a local preference value of 400 to Router3. By default, a local preference value of 100 is advertised. Therefore, Router1 will advertise a local preference of 100 to Router3. Because the local preference of the route through Router2 is higher than the local preference of the route through Router1, Router3 will prefer the route through Router2.
The local preference value can also be specified by using a route map. The route-map map1 permit 10 command configures a route map named map1. The permit keyword indicates that the conditions specified in the set command will be processed, and the 10keyword is a sequence number that specifies the order in which route maps should be processed. Since no match command is specified, the route map will apply to all packets. The set local-preference 300 command configures a local preference value of 300 for routes affected by the route map. Finally, the neighbor 10.40.40.4 route-map map1 in command applies the route-map named map1 to incoming routes from 10.40.40.4. Router2 will then advertise this route to Router3 with a local preference value of 300. Because the local preference of the route through Router2 is higher than the default local preference of the route through Router1, Router3 will prefer the route through Router2.
You cannot accomplish your goal by issuing the following command set:
Router2(config)#route-map map1 permit 10
Router2(config-route-map)#set local-preference 500
Router2(config-route-map)#exit
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.20.20.3 route-map map1 in
In this command set, the neighbor command incorrectly specifies Router3, not Router4, as the neighbor router. Therefore, routes received by Router2 from Router3 would be assigned a local preference value of 500 and advertised to Router4.
You cannot accomplish your goal by issuing the following command set:
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.40.40.4 weight 45000
When determining the best path, a BGP router first chooses the route with the highest weight. By default, routes generated by the local router are assigned a weight of 32768 and routes learned from another BGP router are assigned a weight of 0. Issuing the neighbor 10.40.40.4 weight 45000 command on Router2 would configure the path toward Router4 with a weight value of 45000. However, this weight value is significant only to Router2; it would not be advertised to Router3. Therefore, issuing the neighbor 10.40.40.4 weight 45000 command on Router2 would not influence routing decisions on Router3. Issuing the neighbor 10.20.20.2 weight 45000 command on Router3 would ensure that Router3 preferred the route through Router2.
You cannot accomplish your goal by issuing the following command set, because the neighbor command would configure Router2 with a weight value for the path toward Router3:
Router2(config)#router bgp 100
Router2(config-router)#neighbor 10.20.20.3 weight 45000